A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait


Reducing the metabolic energy of walking and running using an unpowered hip exoskeleton, Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation

The mechanisms and mechanical energy of human gait initiation from the lower-limb joint level perspective
Research articles Scientific Reports

Modeling the Effects of Linear and Torsional Spring Based Passive Assistance on Human Gait

Voluntary changes in step width and step length during human walking affect dynamic margins of stability. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Research articles Scientific Reports

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect
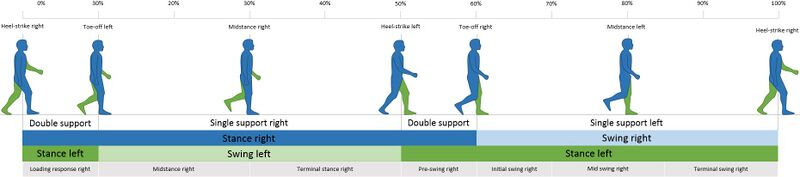
Gait Definitions - Physiopedia

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect

Estimation of quasi-stiffness of the human hip in the stance phase

Estimation of quasi-stiffness of the human hip in the stance phase of walking. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Research articles Scientific Reports

Influence of k S and k D on the foot locations. a) Step length and