Disc Herniation - Physiopedia
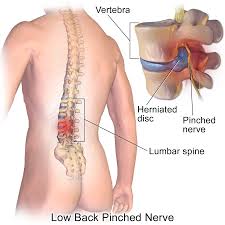
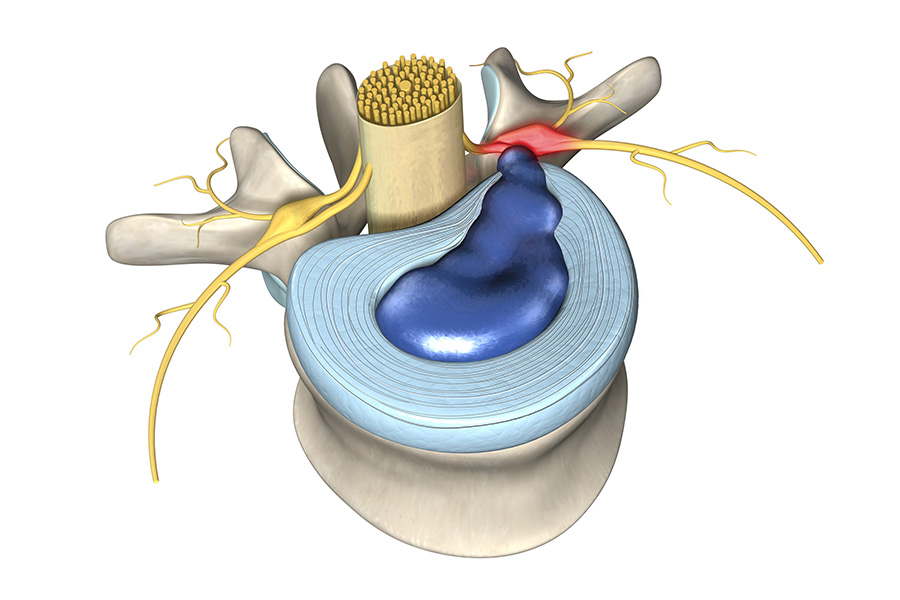
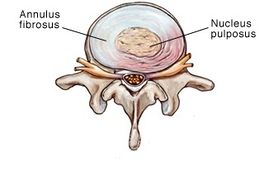
A herniated disc in the spine is a condition during which a nucleus pulposus is displaced from intervertebral space. It is a common cause of back pain. The patient's who experience pain related to a herniated disc often remember an inciting event that caused their pain. Unlike mechanical back pain, herniated disc pain is often burning or stinging, and may radiate into the lower extremity. Furthermore, in more severe cases, there can be associated with weakness or sensation changes. In some instances, a herniated disc injury may compress the nerve or the spinal cord causing pain consistent with nerve compression or spinal cord dysfunction, also known as myelopathy.[1].
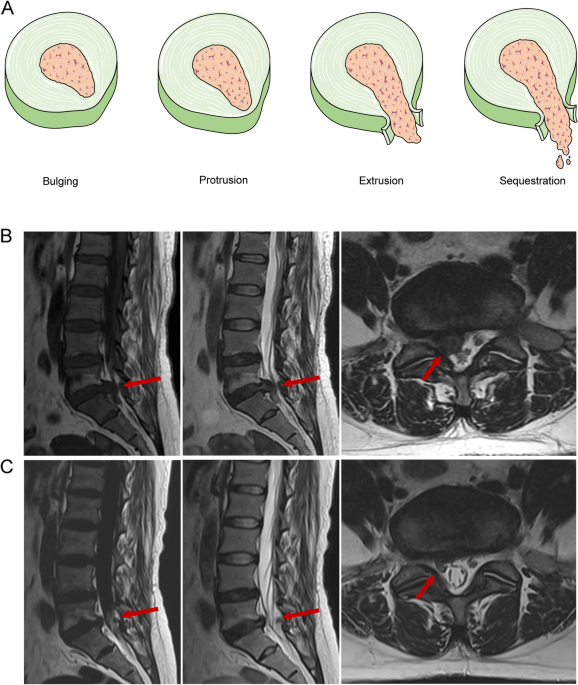
Characteristics and mechanisms of resorption in lumbar disc

Physiopedia on X: The nocebo effect 👉Psychobiological phenomenon
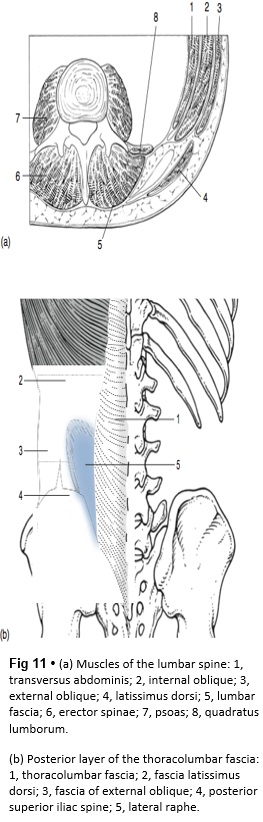
Lumbar Anatomy - Physiopedia

Disc herniation/bulge/prolapse, Kingsley Physio

MedPix Case - Bilateral clinical lumbosacral radiculopathy
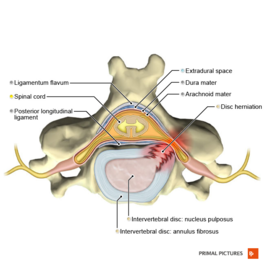
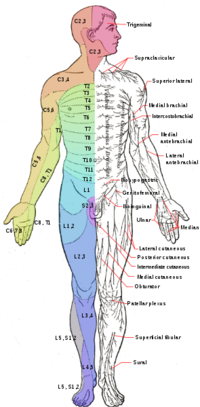
Lumbar Radiculopathy - Physiopedia
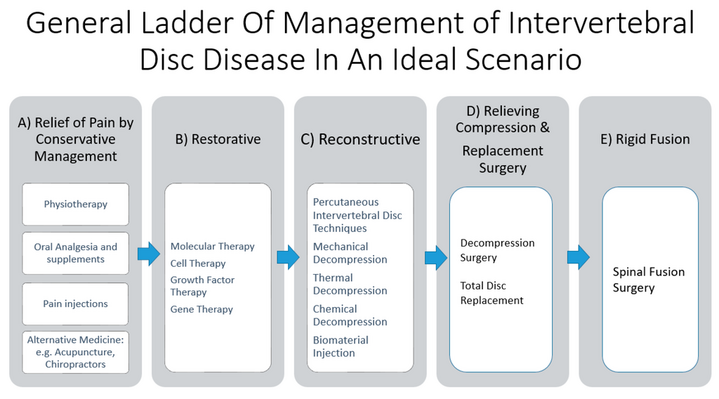
Internal disc disruption - Physiopedia

Cervical Spine Disc Bulge - McKenzie Physio Mobilisation, Tim Keeley
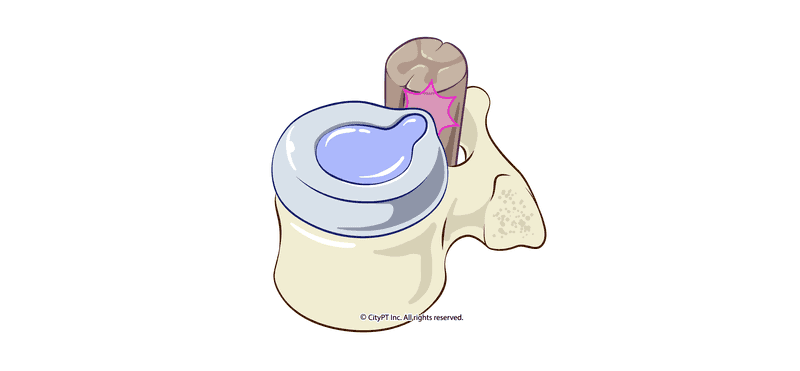
A Physical Therapy Guide to a Herniated Disc - CityPT
Lumbar Radiculopathy - Physiopedia
Disc Herniation - Physiopedia
Cervical Disc Herniation, Cervical Radiculopathy and Cervical
Internal disc disruption - Physiopedia

Thoracic Disc Syndrome - Physiopedia

Thoracic Disc Syndrome - Physiopedia