Emissions of Carbon Dioxide in the Electric Power Sector

HTML Format - At a Glance The electric power sector accounts for about 30 percent of U.S. emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), the most common greenhouse gas. Although demand for electricity is projected to increase as the economy grows and as other sectors rely more heavily on it, the amount of CO2 emitted in producing electricity is likely to decline because that sector has relatively low-cost methods of reducing those emissions.
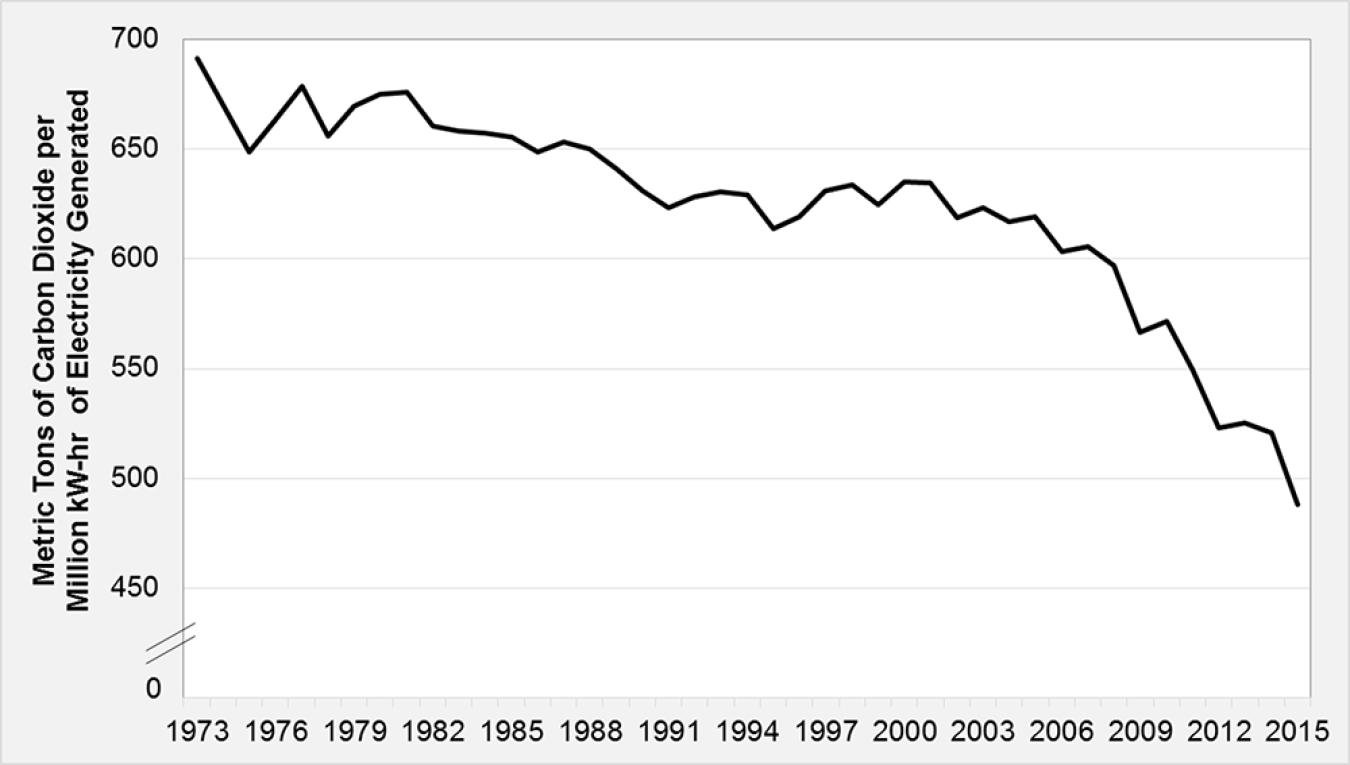
Fact #949: October 31, 2016 Reduced CO2 Emissions in the Electric Power Sector Will Benefit the Transportation Sector as Electrification Grows

How Research Is Used to Assess Policy Proposals at CBO

Emissions of Carbon Dioxide in the Electric Power Sector

Lower US CO2 Emissions Due In Part To Shifts In Power Generation Sources - CleanTechnica
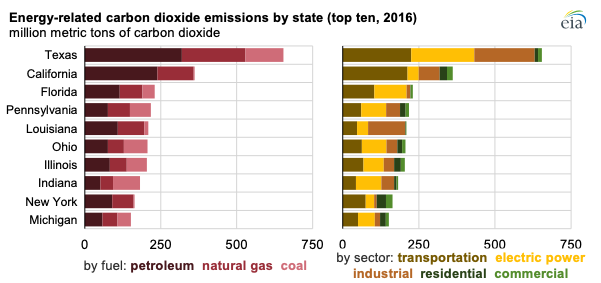
Energy-related carbon dioxide emission profiles differ dramatically from state to state

Global energy policy analysis to achieve near-term climate goals in the United States - ScienceDirect

Carbon dioxide emissions from electricity generation in 2015 were lowest since 1993 - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)

Electric power sector CO2 emissions drop as generation mix shifts from coal to natural gas - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)

Power sector carbon dioxide emissions fall below transportation sector emissions - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
Frontiers Viewpoints on Net-Zero Emissions of Agricultural Energy Internet

Transparency at CBO: Future Plans and a Review of 2022
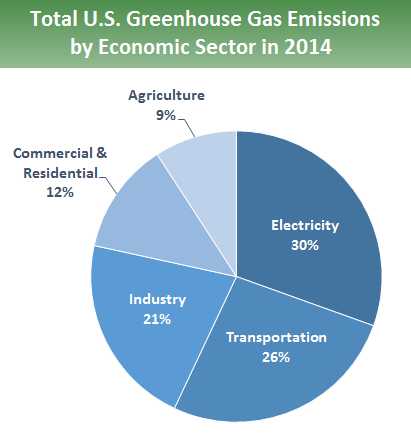
Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions

Emissions of Carbon Dioxide in the Transportation Sector