Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery - The Lancet


Figure 1 from Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as biomarker of acute kidney injury: a review of the laboratory characteristics and clinical evidences
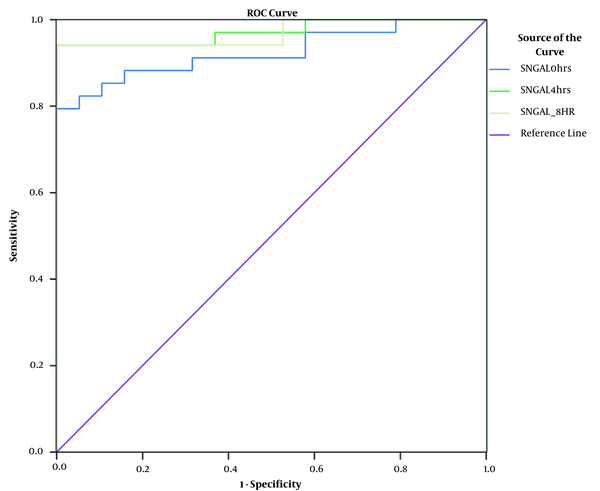
Evaluating Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as an Early Marker of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients, Nephro-Urology Monthly

Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts the efficacy of tolvaptan for ascites in patients with liver cirrhosis

Urinary π-glutathione S-transferase Predicts Advanced Acute Kidney Injury Following Cardiovascular Surgery
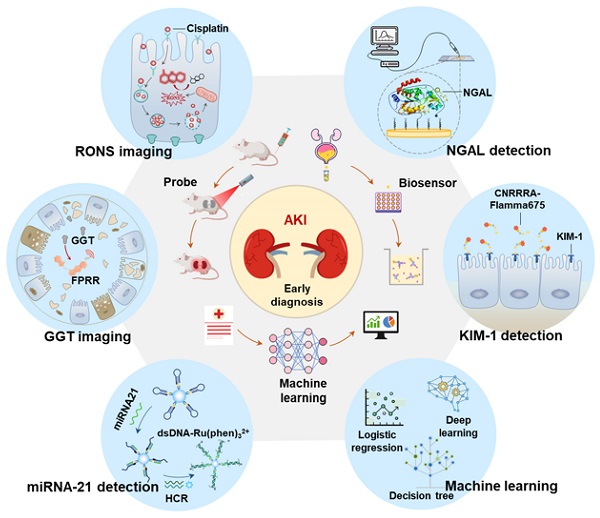
Emerging early diagnostic methods for acute kidney injury

Contemporary Management of Severe Acute Kidney Injury and Refractory Cardiorenal Syndrome: JACC Council Perspectives
Association of Perioperative Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels with 3-Year Mortality after Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
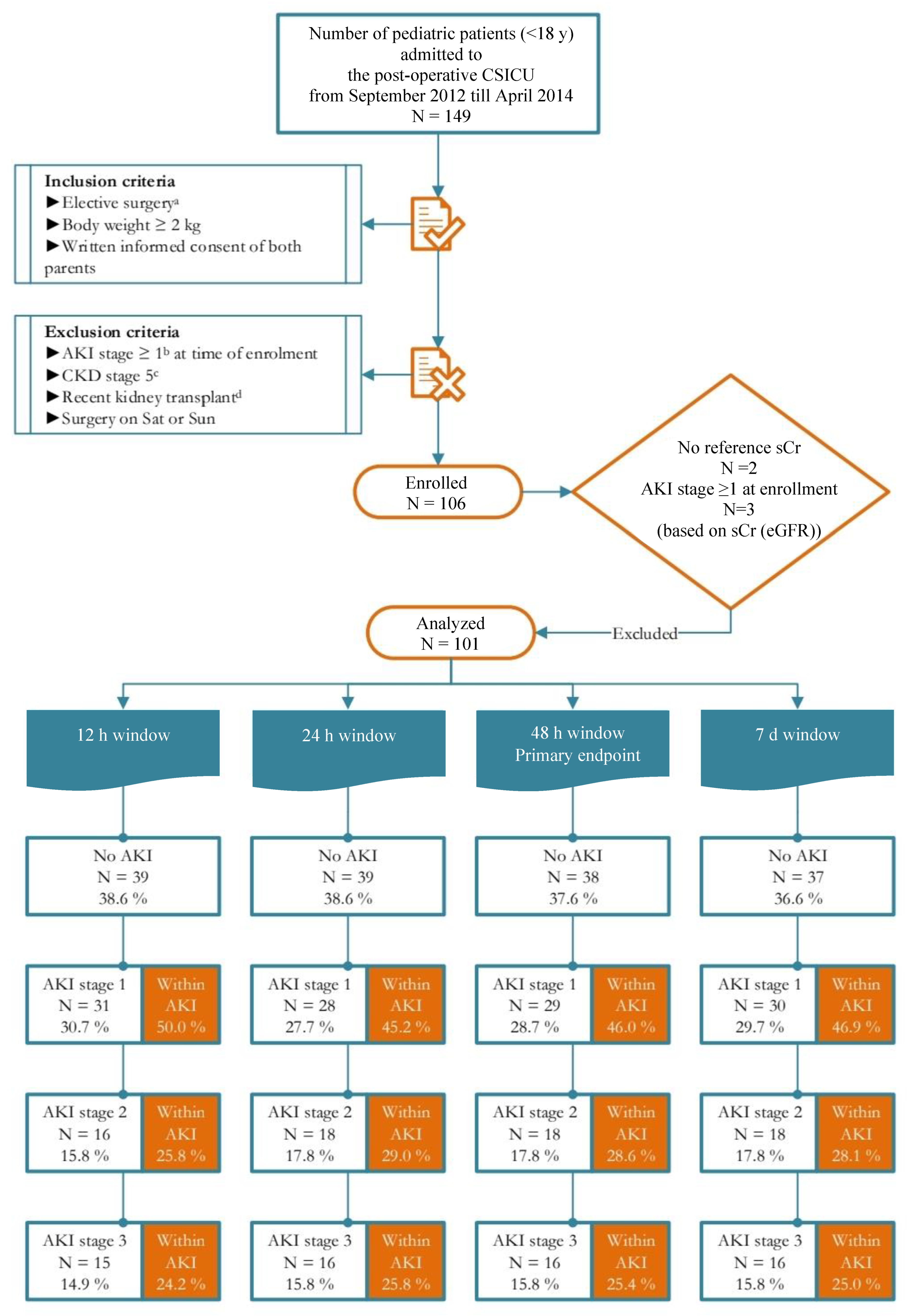
Diagnostics, Free Full-Text

Full article: Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and cystatin C are early biomarkers of acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery
Length of gestation and birth weight are associated with indices of combined kidney biomarkers in early childhood
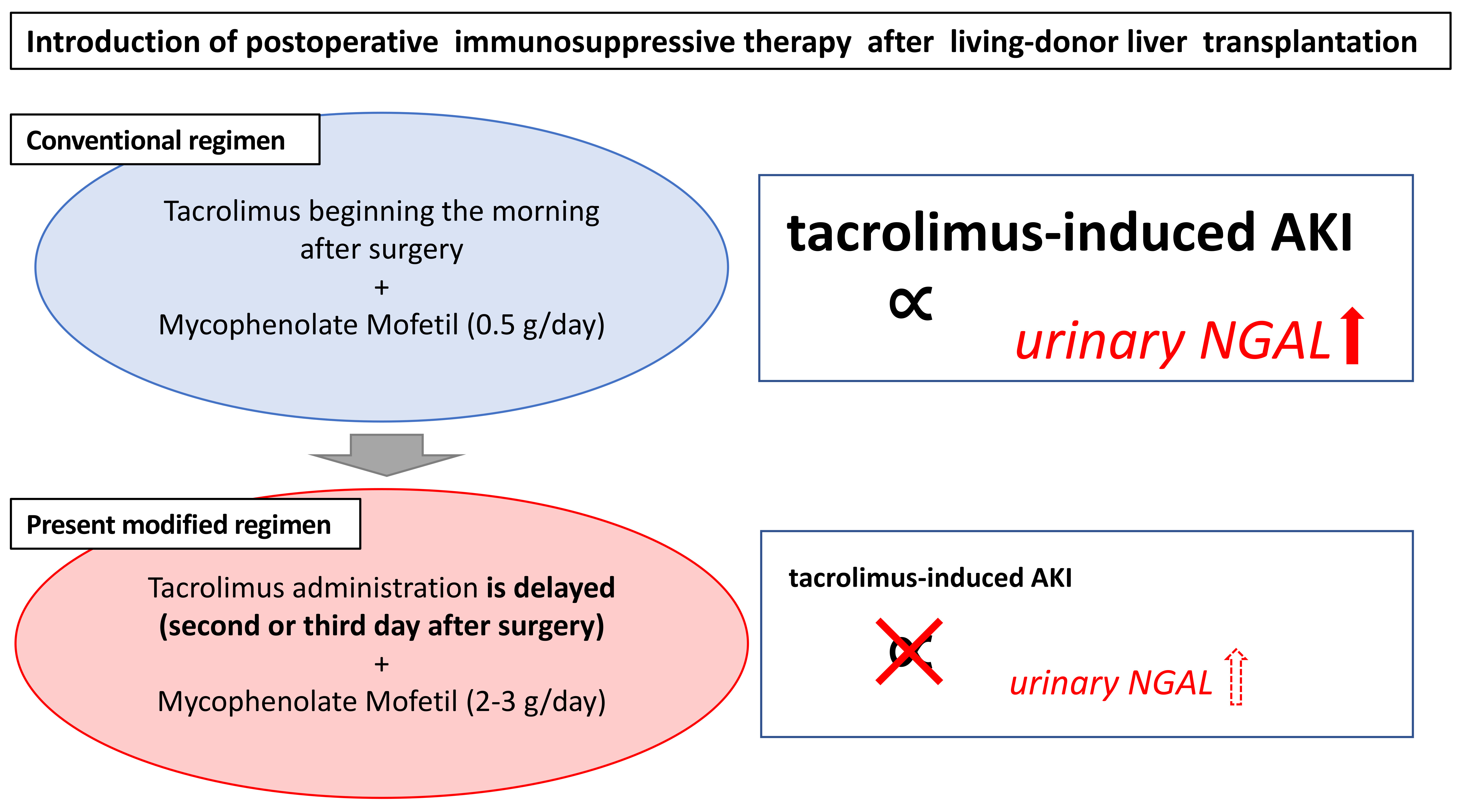
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at 3 hours after return of spontaneous circulation in patients with cardiac arrest and therapeutic hypothermia: early predictor of acute kidney injury, BMC Nephrology