Copper accumulation, translocation, and toxic effects in grapevine

Root system structure as a criterion for the selection of

Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: Rhizosphere processes and

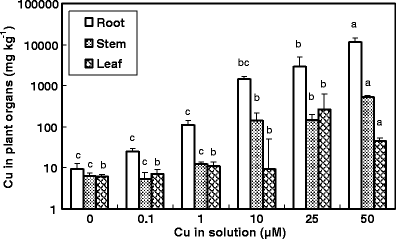
elongation, root dry weight, and leaf dry weight (mean ± standard

Soil application of P can mitigate the copper toxicity in grapevine: physiological implications - ScienceDirect

Multi-omics analyses on the response mechanisms of 'Shine Muscat

Multi-omics analyses on the response mechanisms of 'Shine Muscat' grapevine to low degree of excess copper stress (Low-ECS) - ScienceDirect

Copper: uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants and management of
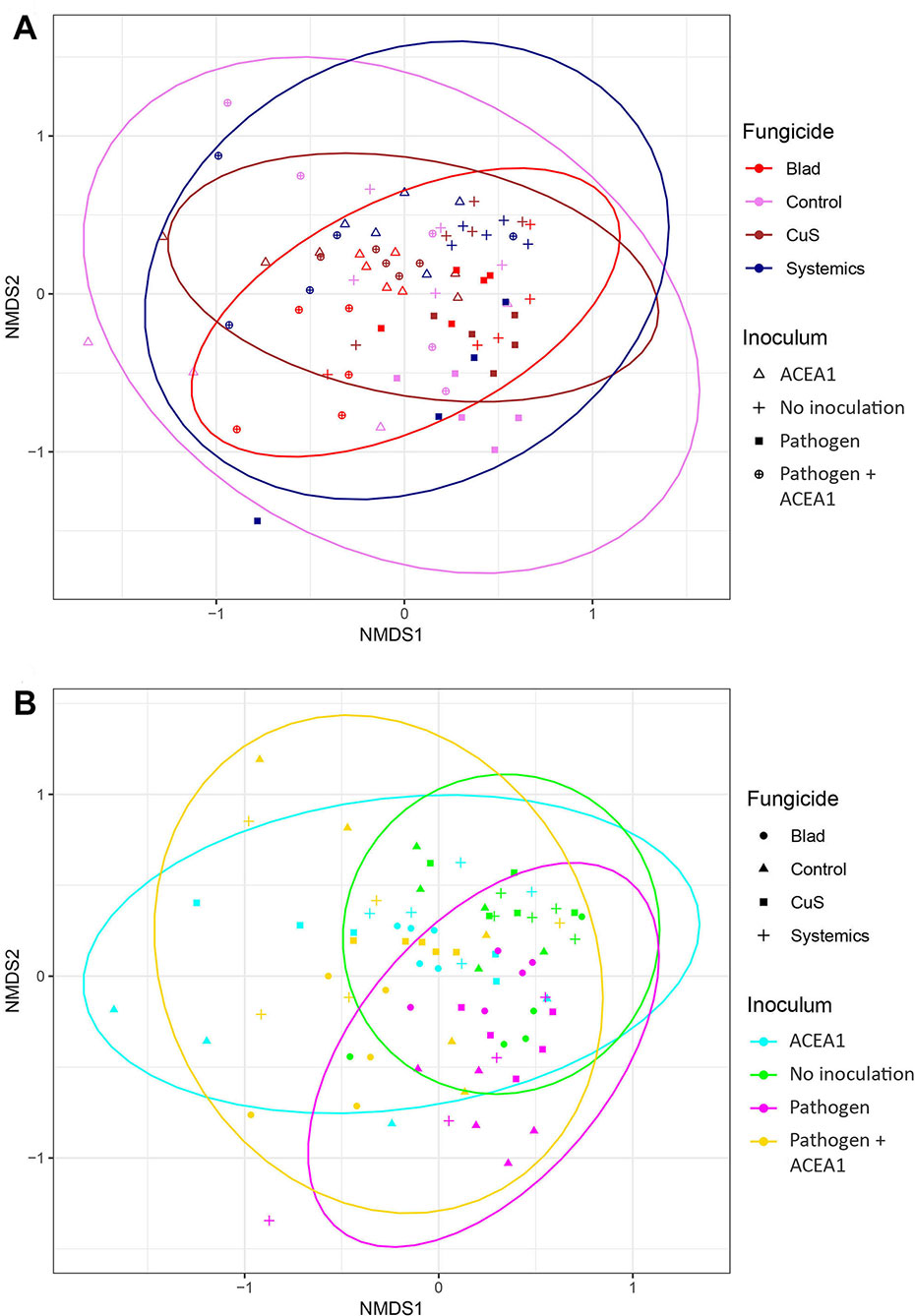
Frontiers Fungicides and the Grapevine Wood Mycobiome: A Case Study on Tracheomycotic Ascomycete Phaeomoniella chlamydospora Reveals Potential for Two Novel Control Strategies
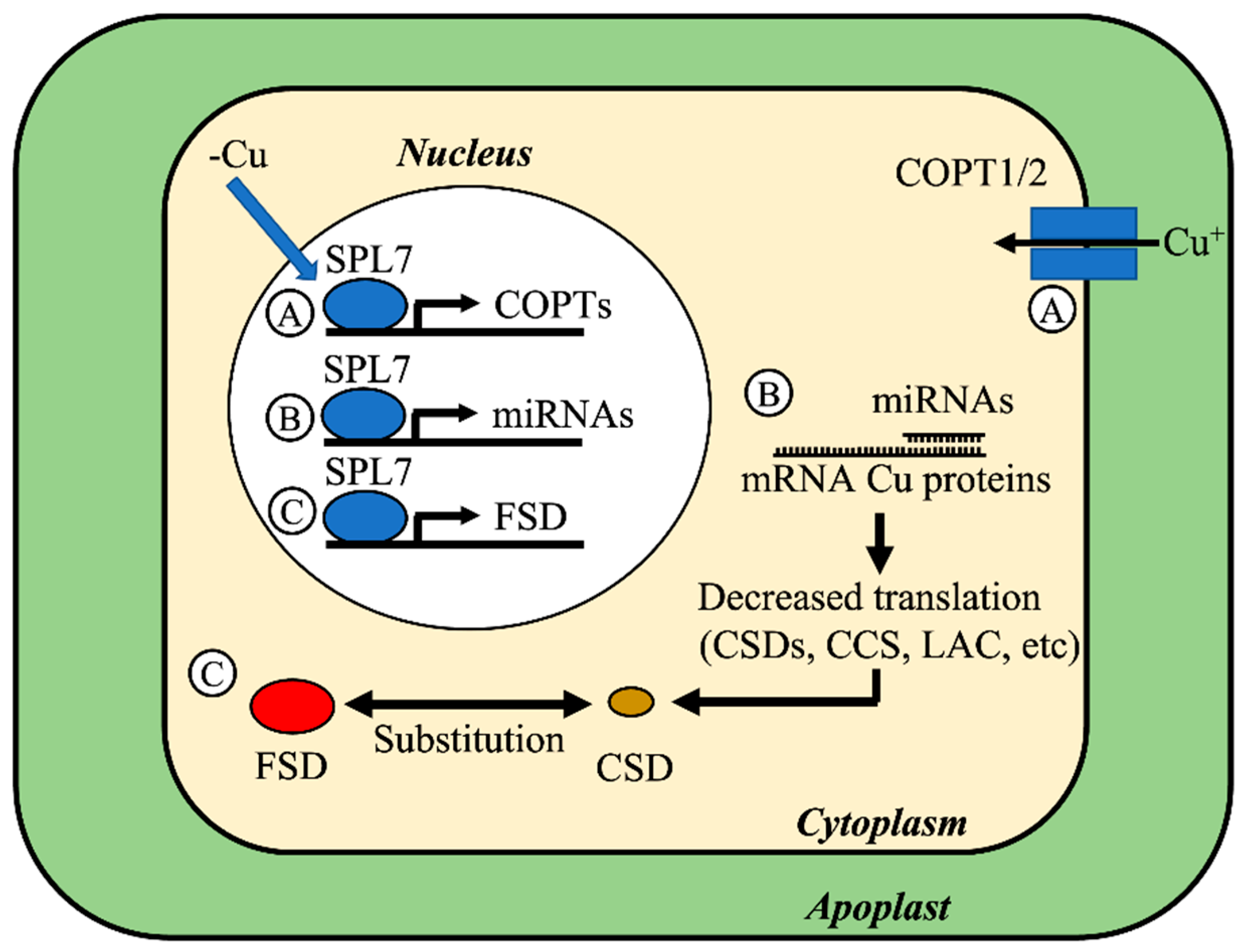
Agronomy, Free Full-Text

PDF) Modeling Alleviative Effects of Ca, Mg, and K on Cu-Induced Oxidative Stress in Grapevine Roots Grown Hydroponically

Germplasm resource evaluation and the underlying regulatory

Malus rootstocks affect copper accumulation and tolerance in trees
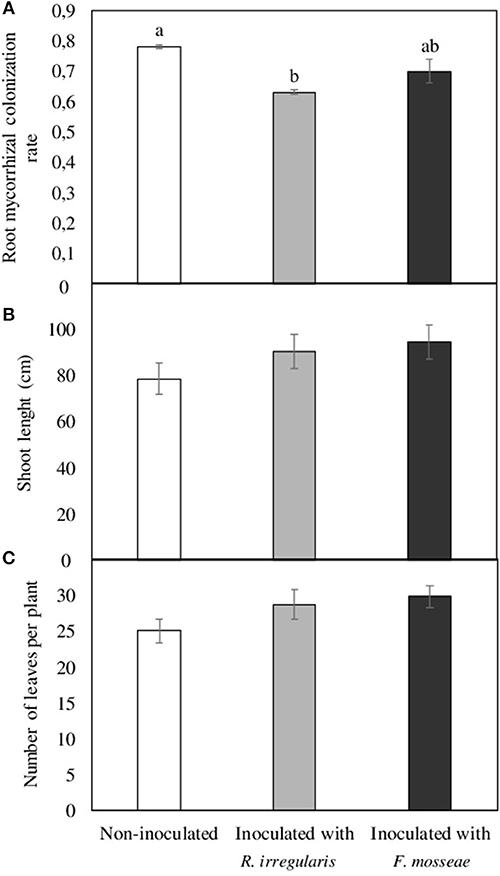
Frontiers Mycorrhizal Inoculation Differentially Affects

Uptake, accumulation, and translocation of Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, Ni, and
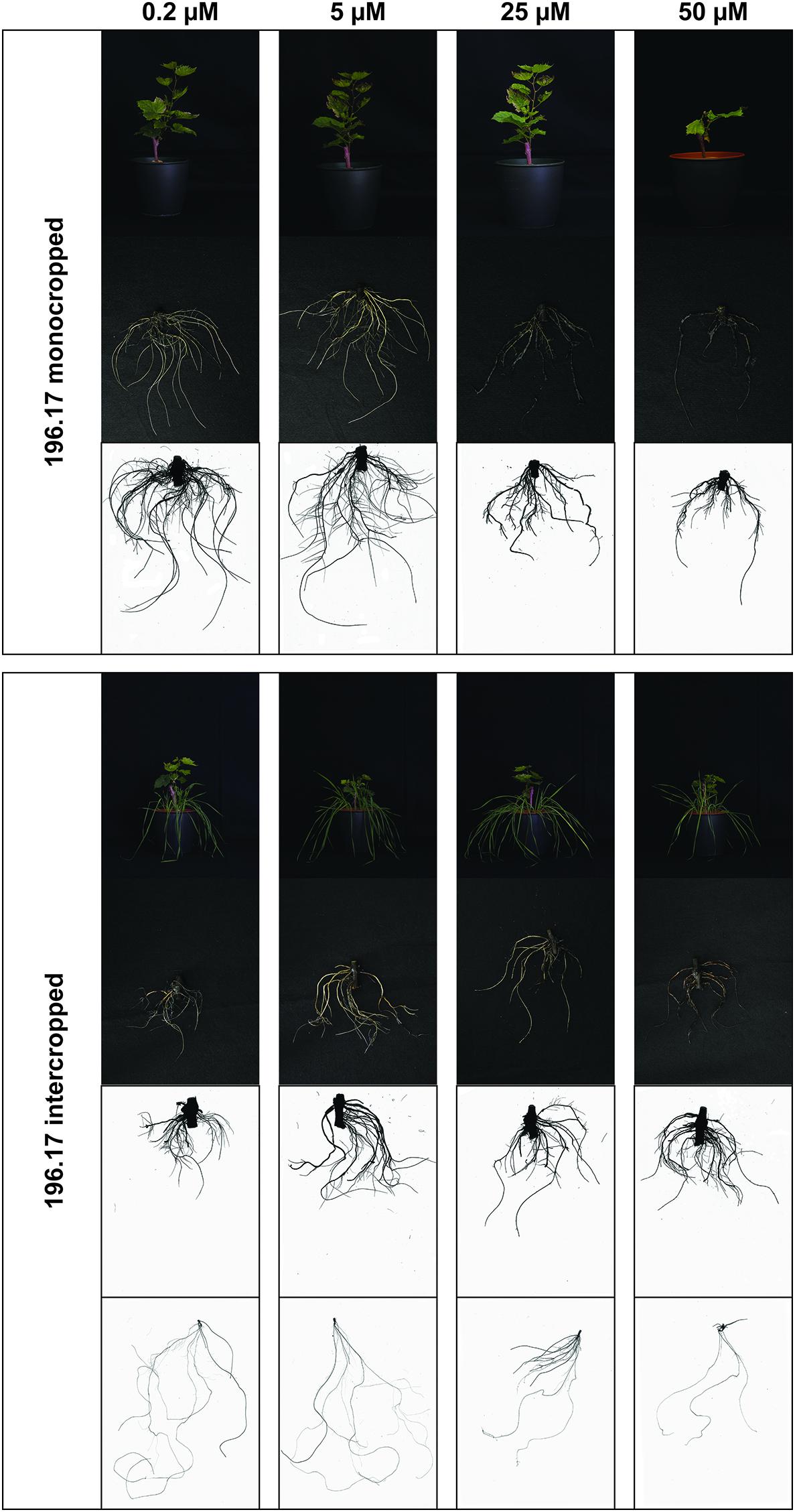
Frontiers Morphological Root Responses and Molecular Regulation of Cation Transporters Are Differently Affected by Copper Toxicity and Cropping System Depending on the Grapevine Rootstock Genotype