Cellular fluorescence intensity and cell size as a function of

Download scientific diagram | | Cellular fluorescence intensity and cell size as a function of enrichment substrate on a subset of basalt enrichments (sample 30R-1A). The circle size indicates the average cellular area (mm 2 ) as measured by epi-fluorescence microscopy. The standard deviation for the cellular area of each sample is roughly 46% based on the following number of cells counts for each treatment: Host Rock (n = 28); No addition (n = 41); CH 3 COONa (n = 38); CH 4 (n = 62); NaHCO 3 (n = 43); NaHCO 3 + NH 4 Cl (n = 39); NaHCO 3 + NaNO 3 (n = 36); NH 4 Cl (n = 35); NaNO 3 (n = 38). Symbols ++ and + indicate analysis of variance P-values of <0.01 and <0.05, respectively, versus Host rock or No addition; and * * indicate P < 0.01 versus CH 3 COONa, CH 4 or NaHCO 3 . from publication: Nitrogen Stimulates the Growth of Subsurface Basalt-associated Microorganisms at the Western Flank of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge | Oceanic crust constitutes the largest aquifer system on Earth, and microbial activity in this environment has been inferred from various geochemical analyses. However, empirical documentation of microbial activity from subsurface basalts is still lacking, particularly in the | Nitrogen, Stimulation and Geomicrobiology | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
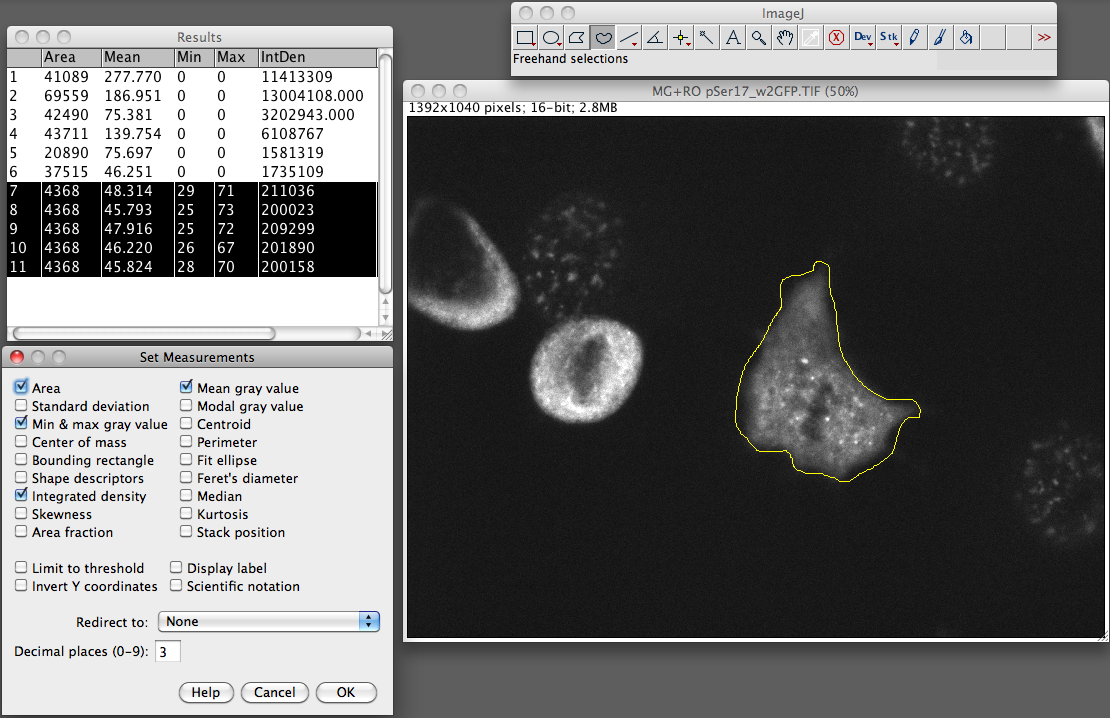
Measuring cell fluorescence using ImageJ — The Open Lab Book v1.0
Cells, Free Full-Text

PDF) Nitrogen Stimulates the Growth of Subsurface Basalt
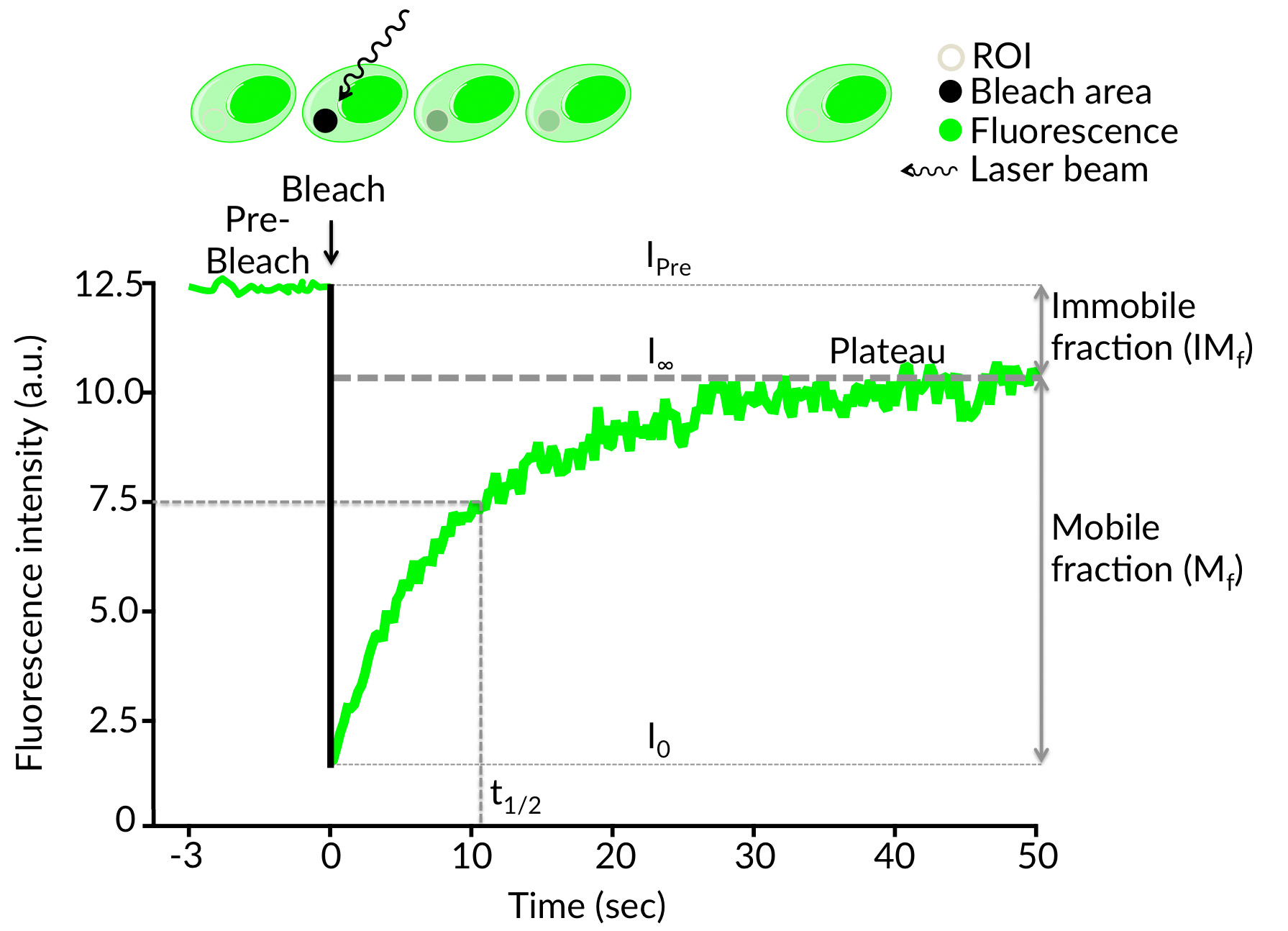
FrapBot Features
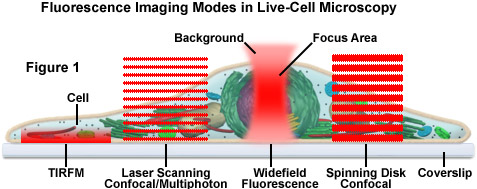
ZEISS Microscopy Online Campus, Live-Cell Imaging

Microscope Resolution: Concepts, Factors and Calculation, Science Lab

PDF) Nitrogen Stimulates the Growth of Subsurface Basalt

Katrina EDWARDS University of Southern California, California

a) Average fluorescence intensity per cell, and (b) percentage of
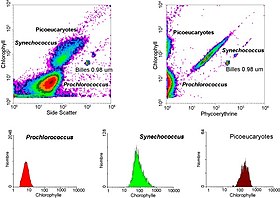
Flow cytometry - Wikipedia

Cellular fluorescence intensity and cell size as a function of

PDF) Nitrogen Stimulates the Growth of Subsurface Basalt

Versatile phenotype-activated cell sorting

Sequential patterns of microbial degradation of complex organic