The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der

For 1 mol of a gas, the van der Waals equation is (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))(V(m)-b)=RT Ignoring b, we get (given volume of gas molecule is negligible) (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))V(m)=RT ltbgt or pV(m)+(a)/(V(m))=RT or (pV(m))/(RT)+(a)/(V(m)RT)=1 or Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=1-(a)/(V(m)RT) (i) It is given that Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=0.5implies V(m)=(0.5RT)/(P) With this, equation (i) becomes 0.5=1-(a)/((0.5RT//p)RT) or a=(0.5)((0.5RT)/(p))RT=0.25(R^(2)T^(2))/(p) Substiuting the given values, we get a=(0.25)[((0.082L atm K^(-1)mol^(-1))^(2)(273 K)^(2))/((100 atm))] =1.2528 L^(2) atm mol^(-2)

To an evacuated vessel with movable piston under external pressure of

Malayalam] The compressibility factor for definite amount of van der
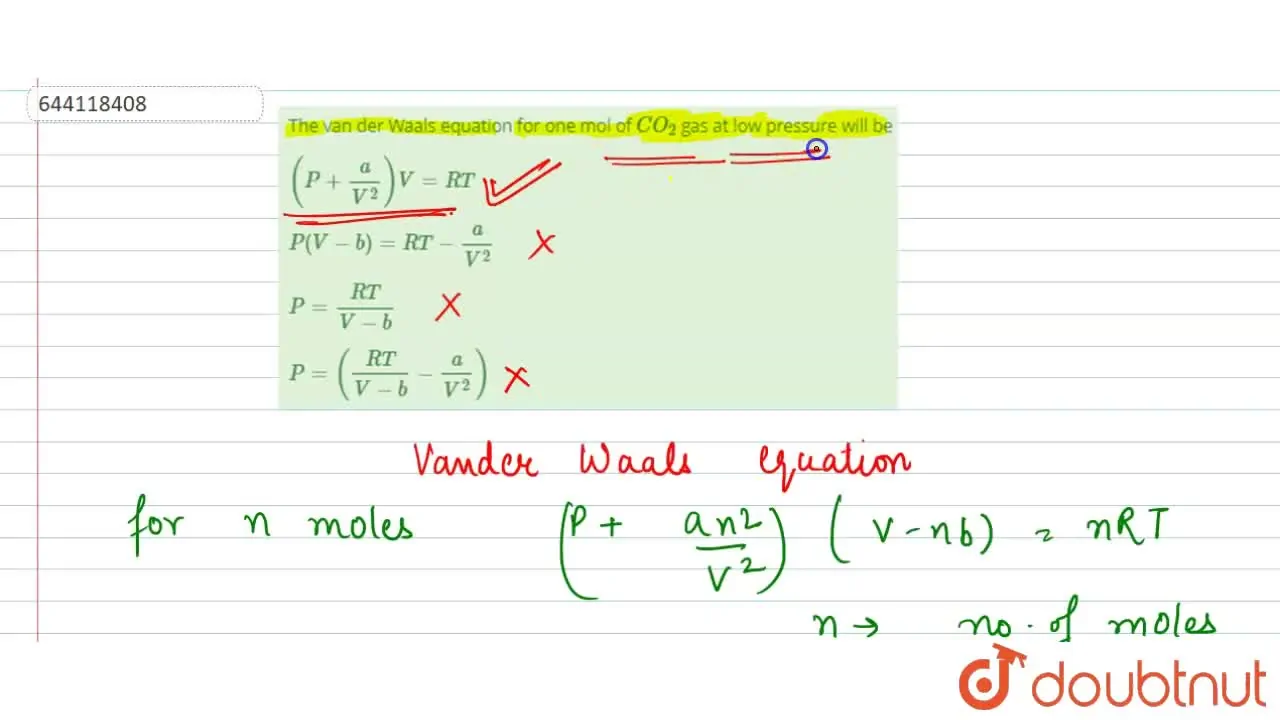
The van der Waals equation for one mol of CO(2) gas at low pressure wi

When 3.2 gm of sulphur is vapourized at 450^(@)C and 723 mm pressure
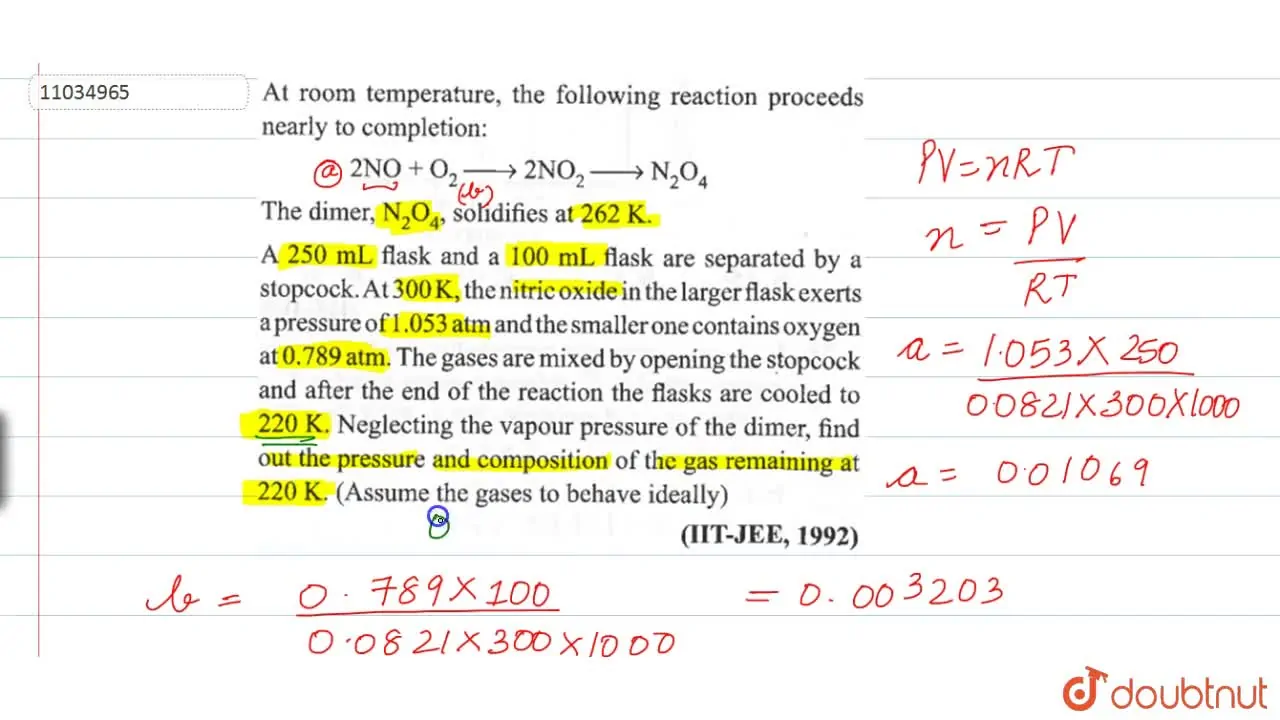
At room temperature, the following reaction proceeds nearly to complet

The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der

The root mean square velocity of the molecule is inversely proportiona

The final product Z in the following reaction is
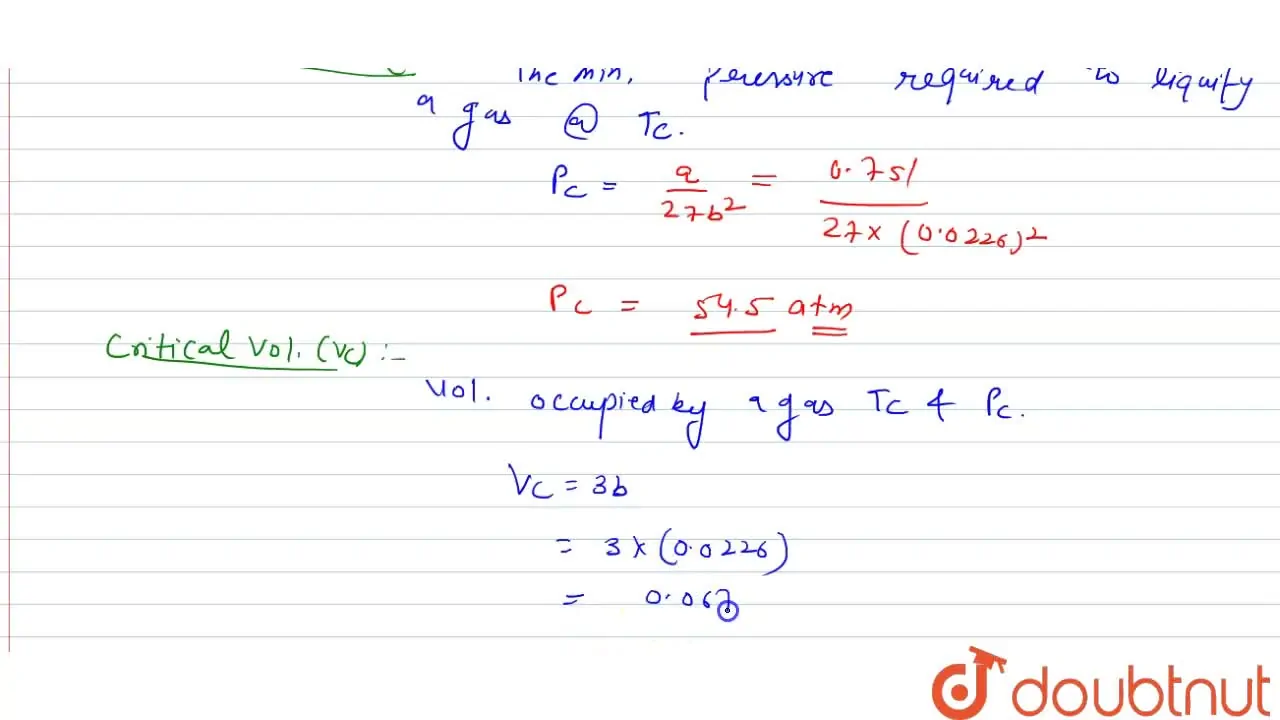
Calculate the critical constants of a gas whose van der Waals constant

A 672 ml of a mixture of oxygen - ozone at N.T.P. were found to be wei