How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?
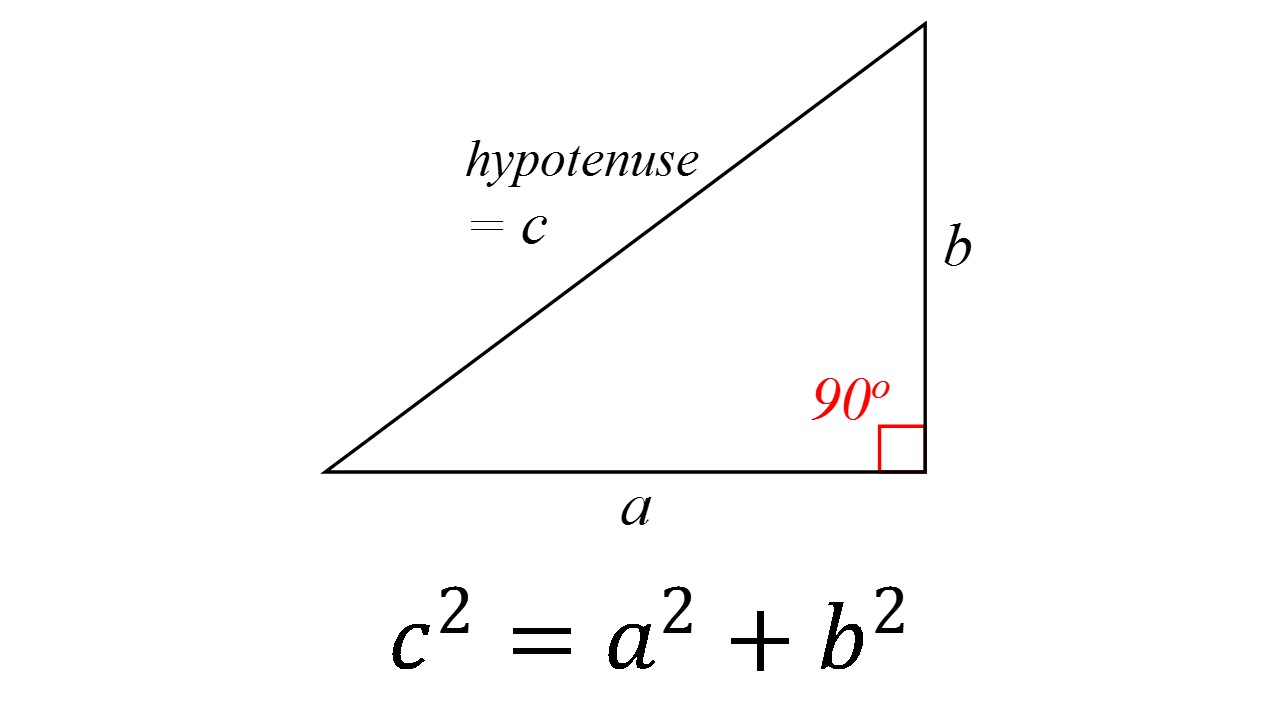
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.

Can you help please!!! The Pythagorean theorem states that in any
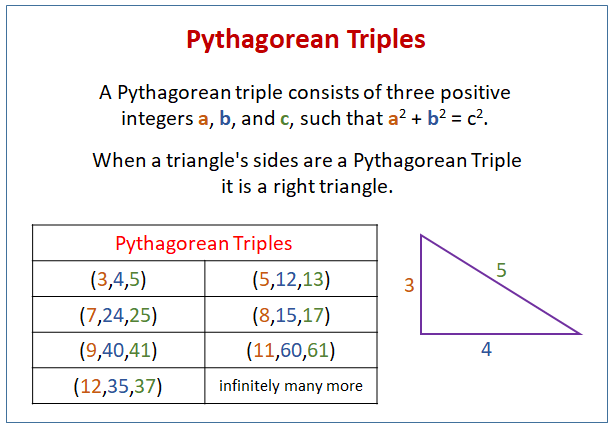
Pythagorean Triples (video lessons, examples, step-by-step solutions)
How to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle

The Pythagorean Theorem

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the missing side of the

5 Ways to Find the Length of the Hypotenuse - wikiHow

3-4-5 Triangles, Definition, Rule & Angles - Lesson
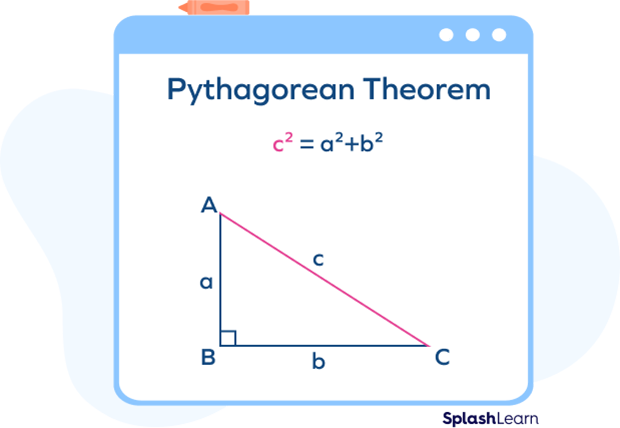
Pythagorean Triples - Definition, Formula, Examples, Facts
What is the Pythagorean theorem, and how is it used to solve
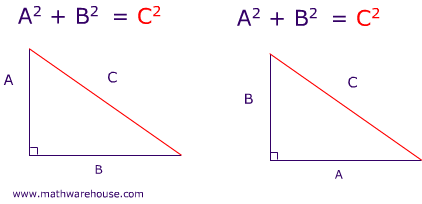
A right triangle's leg is 9 and the hypotenuse is 15, what is the