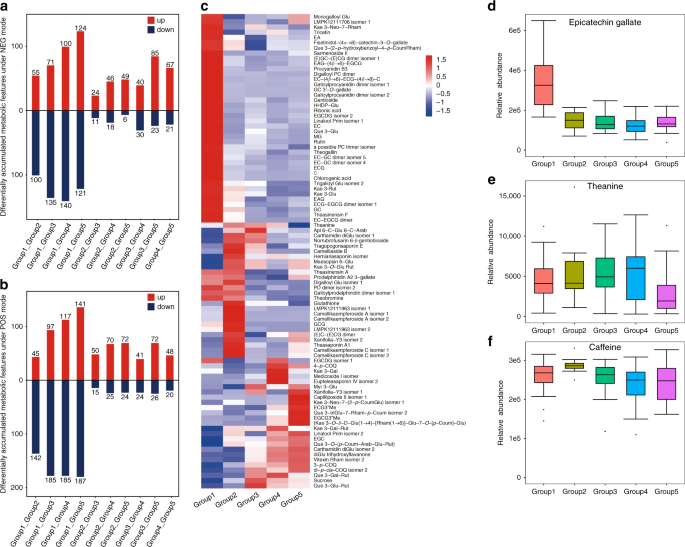
Metabolite signatures of diverse Camellia sinensis tea populations

Frontiers From the Wild to the Cup: Tracking Footprints of the Tea Species in Time and Space
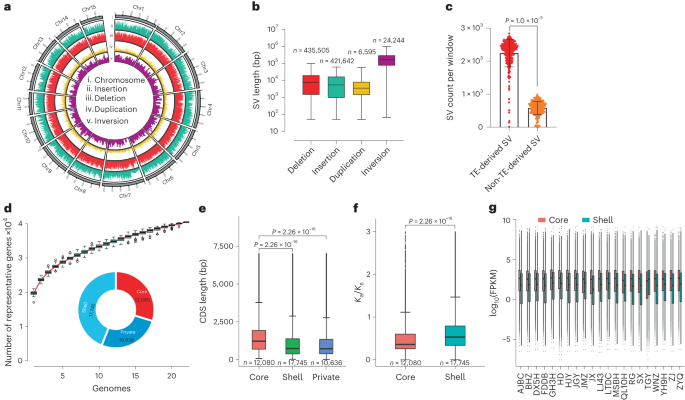
Gene mining and genomics-assisted breeding empowered by the pangenome of tea plant Camellia sinensis

Processing, chemical signature and food industry applications of Camellia sinensis teas: An overview - ScienceDirect

Metabolomic and Pathway Changes in Large‐Leaf, Middle‐Leaf and Small‐Leaf Cultivars of Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze var. niaowangensis - Wang - 2021 - Chemistry & Biodiversity - Wiley Online Library

An undefined cystatin CsCPI1 from tea plant Camellia sinensis harbors antithrombotic activity - ScienceDirect

Insights into the Key Odorants in Large-Leaf Yellow Tea (Camellia sinensis) by Application of the Sensomics Approach
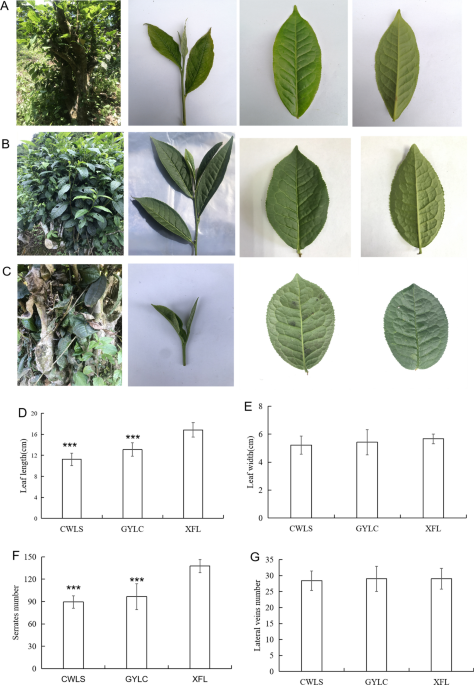
Molecular identification of Lingyun Baihao wild and cultivated tea through genome-wide sequencing
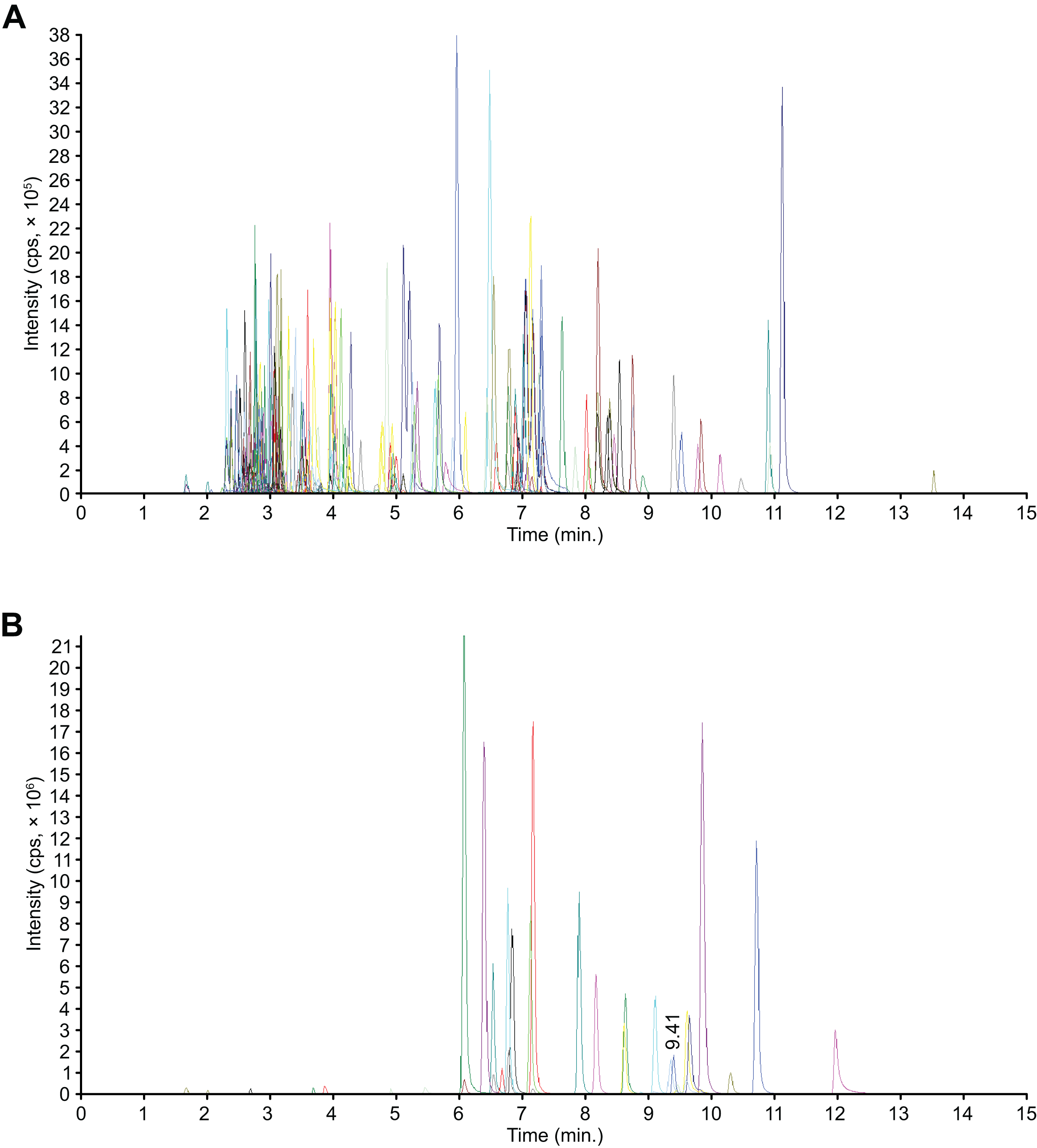
Metabolomics study of flavonoids in Coreopsis tinctoria of different origins by UPLC–MS/MS [PeerJ]

PDF) The Antimethanogenic Potentials of Plant Extracts: Their Yields and Phytochemical Compositions as Affected by Extractive Solvents

Processing, chemical signature and food industry applications of Camellia sinensis teas: An overview - ScienceDirect

RNA Methylome Reveals the m6A-Mediated Regulation of Flavor Metabolites in Tea Leaves under Solar-Withering

Landscapes of the main components, metabolic and microbial signatures, and their correlations during pile-fermentation of Tibetan tea - ScienceDirect
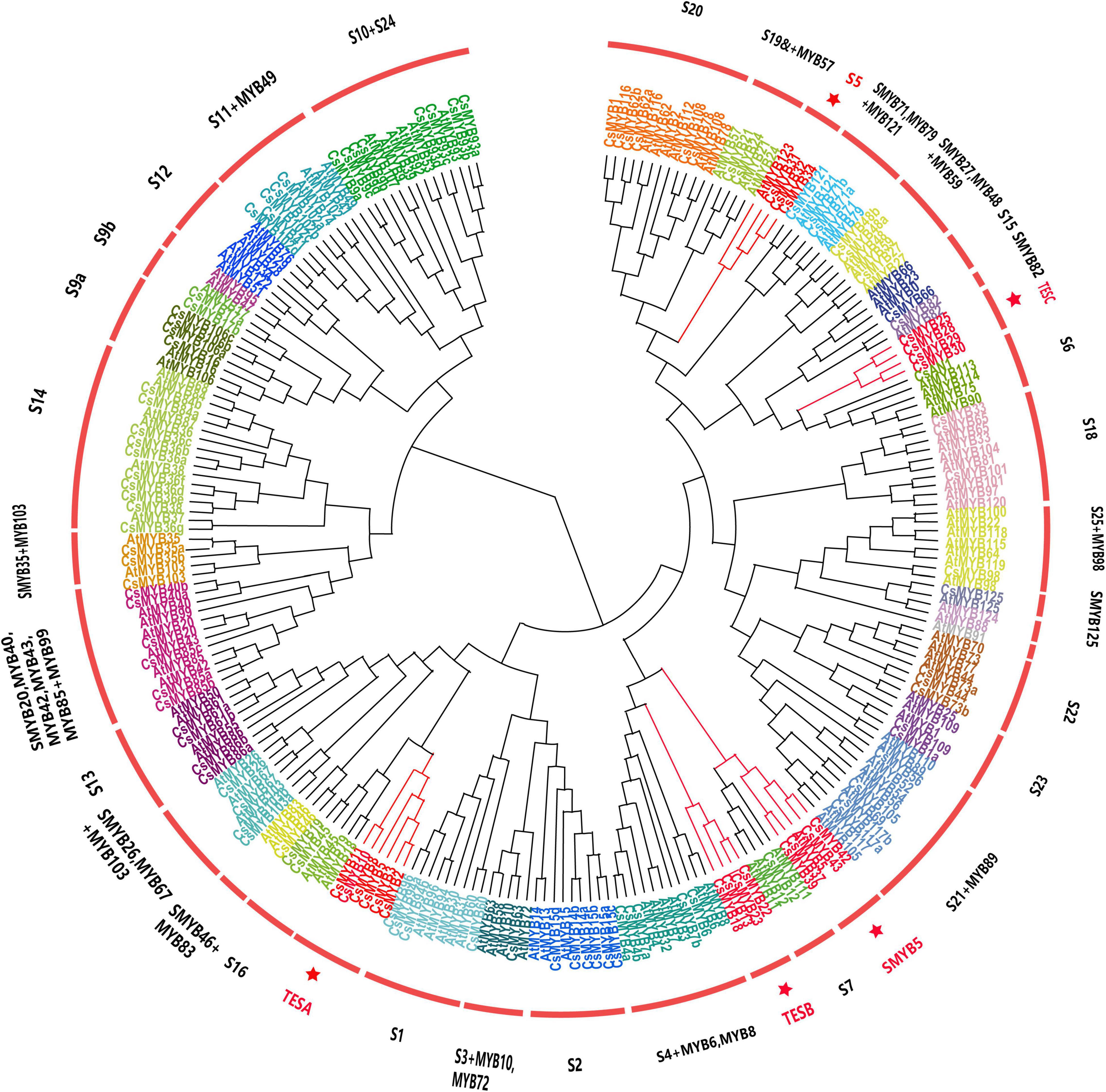
Frontiers Systematic Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Family in Camellia sinensis: Evidence for Galloylated Catechins Biosynthesis Regulation
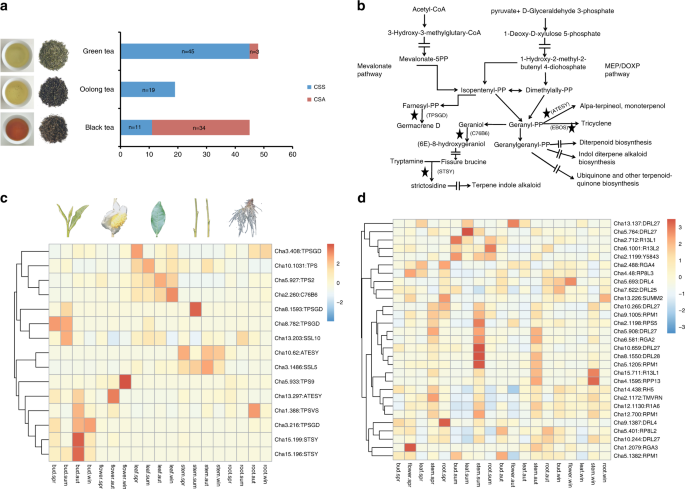
Population sequencing enhances understanding of tea plant evolution
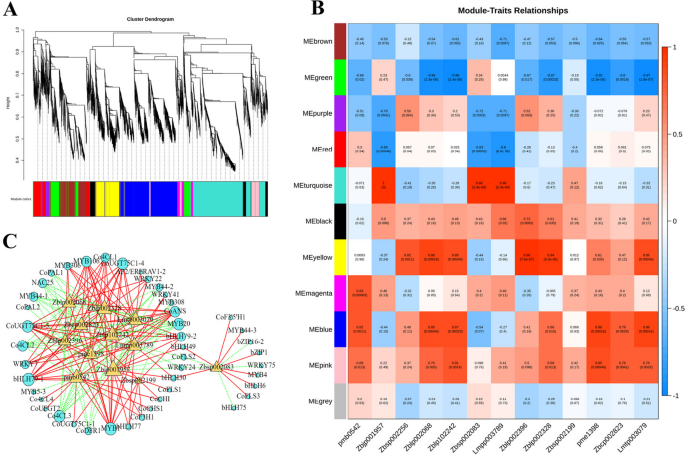
Integrative metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the coloration mechanism in Camellia oleifera petals with different color, BMC Plant Biology